Example
After omission
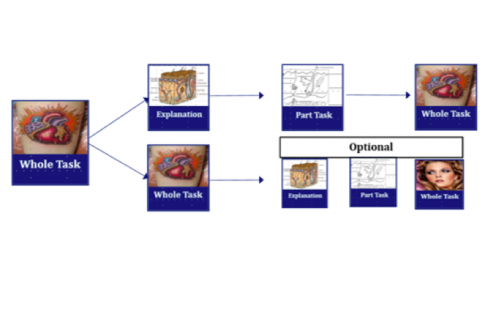
The teacher starts with the introduction of the whole task (how deep pricking?), about which students briefly think for themselves. This will be followed by explanation and sub-tasks, after which pupils themselves will make the whole task.